Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) is a patient-centered‚ evidence-based approach developed by Gregory Johnson and Vicky Saliba Johnson. It integrates manual techniques to enhance mobility‚ reduce pain‚ and restore function by addressing mechanical‚ neuromuscular‚ and motor control systems. This holistic method emphasizes hands-on therapy‚ clinical reasoning‚ and personalized care to optimize movement and overall well-being.
1.1 Definition and Overview
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) is a comprehensive‚ evidence-based approach developed by Gregory Johnson and Vicky Saliba Johnson. It integrates manual techniques with a focus on enhancing mobility‚ reducing pain‚ and restoring function. This patient-centered method addresses the interconnected systems of the body‚ emphasizing mechanical capacity‚ neuromuscular function‚ and motor control. FMT is rooted in clinical reasoning and hands-on therapy‚ making it a holistic approach to improving movement and overall well-being.
1.2 Historical Development
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) was developed by Gregory Johnson and Vicky Saliba Johnson‚ co-founders of the Institute of Physical Art (IPA). This dynamic‚ evidence-based approach evolved from their extensive research and clinical experience. FMT integrates manual techniques with a focus on enhancing mobility and brain-controlled movement to address musculoskeletal issues. Its development emphasizes a holistic understanding of the body’s interconnected systems‚ blending Eastern and Western medical principles to create a comprehensive treatment framework.
1.3 Key Principles and Philosophy
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) is rooted in the belief that the body’s systems are deeply interconnected. Its philosophy emphasizes restoring balance and efficiency through manual techniques that address mechanical capacity‚ neuromuscular function‚ and motor control. By integrating these components‚ FMT aims to optimize movement and reduce pain. The approach is patient-centered‚ focusing on individualized care and evidence-based methods to enhance overall function and well-being.
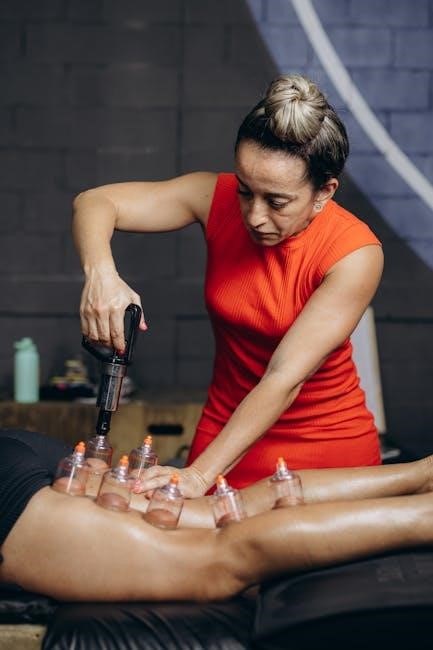

Core Components of Functional Manual Therapy
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) focuses on three key components: mechanical capacity‚ neuromuscular function‚ and motor control; It systematically integrates these elements to restore mobility and optimal function.
2.1 Mechanical Capacity
Mechanical capacity in Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) refers to the body’s ability to move efficiently through its full range of motion. This component focuses on identifying and addressing restrictions in joints‚ soft tissues‚ muscles‚ and visceral structures that limit mobility. By restoring mechanical capacity‚ FMT aims to reduce stiffness‚ improve flexibility‚ and enhance overall movement patterns‚ laying the foundation for optimal physical function and pain-free movement.
- Targets joint and soft tissue mobility.
- Addresses restrictions in muscles and visceral structures.
- Aims to restore efficient movement patterns.
2.2 Neuromuscular Function
In Functional Manual Therapy (FMT)‚ neuromuscular function focuses on the interaction between muscles and the nervous system to achieve efficient movement. This component assesses and addresses dysfunctions in muscle activation‚ strength‚ and coordination. Techniques like neuromuscular re-education help restore proper muscle firing patterns‚ enhancing motor control and reducing pain. By improving neuromuscular function‚ FMT aims to optimize movement efficiency and overall physical function‚ ensuring muscles work synergistically for balanced and pain-free mobility.
2.3 Motor Control
Motor control in Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) focuses on restoring proper movement patterns and efficiency. It involves re-educating the brain and body to execute movements effectively‚ reducing compensatory strategies. Techniques aim to enhance brain-controlled movement‚ ensuring muscles activate appropriately for specific tasks. By improving motor control‚ FMT helps patients achieve sustainable functional improvements‚ enabling them to perform daily activities and sports with optimal efficiency and reduced risk of injury or pain.
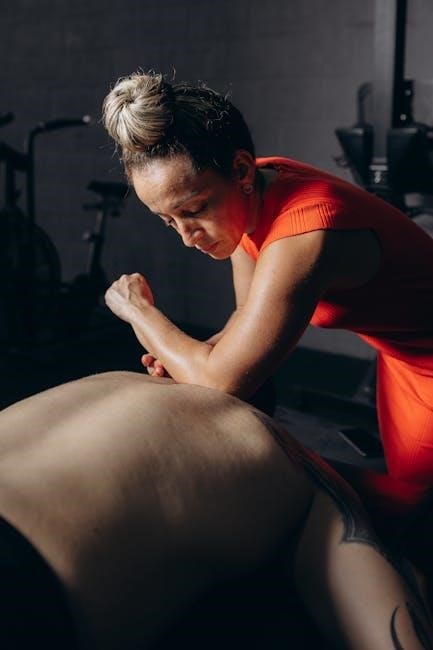
Techniques and Methods in FMT
Functional Manual Therapy employs techniques like soft tissue mobilization‚ joint mobilization‚ neuromuscular re-education‚ and visceral mobilization to restore mobility and function‚ addressing the body’s interconnected systems.
3.1 Soft Tissue Mobilization
Soft tissue mobilization in FMT focuses on manipulating muscles‚ tendons‚ ligaments‚ and fascia to improve mobility and reduce pain. Techniques include massage‚ fascial release‚ and targeted manual interventions to restore normal tissue glide and elasticity. This approach addresses restrictions in soft tissues‚ enhancing joint mobility and overall movement patterns; It is often the initial step in FMT‚ laying the foundation for more advanced interventions like joint mobilization and neuromuscular re-education.
3.2 Joint Mobilization
Joint mobilization in FMT involves targeted manual techniques to improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness. It addresses mechanical restrictions‚ enhancing movement and reducing pain. This hands-on approach focuses on restoring normal joint function‚ ensuring optimal range of motion and alignment. By improving joint mechanics‚ it supports overall musculoskeletal balance and facilitates better movement patterns‚ making it a cornerstone of FMT alongside soft tissue work and neuromuscular strategies.
3.3 Neuromuscular Re-education
Neuromuscular re-education in FMT focuses on restoring optimal muscle function and movement patterns. It involves targeted exercises and manual techniques to enhance brain-muscle communication‚ improving strength‚ coordination‚ and control. This process helps patients regain efficient movement‚ reduce pain‚ and prevent future injuries. By addressing neuromuscular imbalances‚ FMT promotes long-term recovery and functional independence‚ tailored to each patient’s specific needs and goals.
3.4 Visceral Mobilization
Visceral mobilization in FMT targets the mobility of internal organs and their surrounding fascia. It addresses restrictions in visceral movement that may contribute to musculoskeletal dysfunction. By improving organ mobility‚ this technique enhances overall bodily function‚ reduces pain‚ and promotes healing. Visceral mobilization is often used alongside other FMT methods to restore balance and optimize the body’s interconnected systems‚ ensuring comprehensive care for patients with complex conditions.
Certification and Education in FMT
Certification in FMT is offered through the Institute of Physical Art (IPA)‚ requiring intensive education and hands-on training. The Certified Functional Manual Therapist (CFMT) distinction ensures expertise in FMT principles and techniques‚ with less than 300 certified professionals in the U.S.‚ highlighting its exclusivity and rigorous standards.
4.1 Certified Functional Manual Therapist (CFMT)
The Certified Functional Manual Therapist (CFMT) designation is awarded to professionals who complete the Institute of Physical Art’s rigorous education and training. This certification ensures expertise in FMT principles‚ including mechanical capacity‚ neuromuscular function‚ and motor control. The CFMT program involves intensive hands-on training and a comprehensive exam‚ reflecting the founders’ commitment to advancing manual therapy. With fewer than 300 certified professionals in the U.S.‚ it underscores the program’s exclusivity and high standards.
4.2 The Role of the Institute of Physical Art (IPA)
The Institute of Physical Art (IPA) is a leading organization in advancing Functional Manual Therapy (FMT). Founded by Gregory Johnson and Vicky Saliba Johnson‚ IPA provides comprehensive education‚ certification programs‚ and clinical training. It emphasizes evidence-based practices‚ hands-on techniques‚ and patient-centered care. IPA’s rigorous curriculum and certification process ensure therapists master FMT principles‚ while its global outreach promotes the integration of manual therapy into modern healthcare systems‚ fostering innovation and excellence in physical therapy practices worldwide.
4.3 Continuing Education and Advanced Training
Continuing education and advanced training are crucial for mastering Functional Manual Therapy (FMT). The Institute of Physical Art (IPA) offers specialized courses‚ workshops‚ and certification programs to refine therapists’ skills. These programs emphasize hands-on techniques‚ clinical reasoning‚ and evidence-based practices. Advanced training focuses on integrating the latest research and techniques into patient care‚ ensuring therapists stay updated and proficient in delivering effective‚ patient-centered treatments. Ongoing education fosters professional growth and enhances patient outcomes.
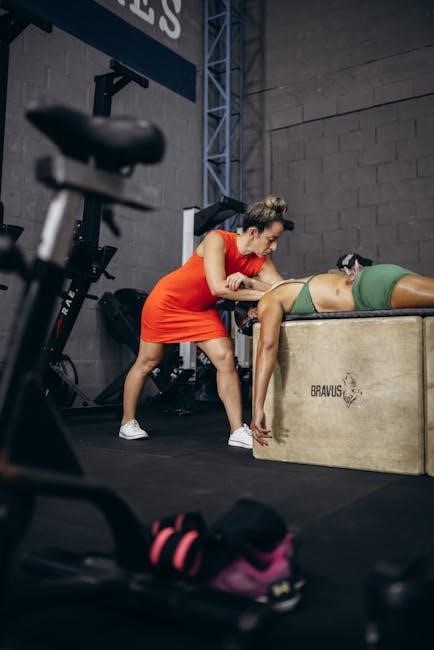

Applications of Functional Manual Therapy
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) is widely applied in chronic pain management‚ sports injuries‚ and post-surgical rehabilitation. It enhances mobility‚ reduces pain‚ and restores function‚ improving overall well-being.
5.1 Chronic Pain Management
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) is highly effective in managing chronic pain by addressing underlying mechanical and neuromuscular dysfunctions. It enhances joint mobility‚ reduces soft tissue restrictions‚ and restores efficient movement patterns. FMT’s holistic approach focuses on identifying and treating the root causes of pain‚ promoting long-term relief and improved function. This method is particularly beneficial for patients with persistent discomfort‚ offering a patient-centered strategy to alleviate pain and enhance overall well-being.
5.2 Sports Injuries and Rehabilitation
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) is a valuable approach in managing sports injuries and rehabilitation; It focuses on restoring joint mobility‚ optimizing neuromuscular control‚ and retraining efficient movement patterns. FMT helps athletes recover from injuries by addressing mechanical and functional limitations‚ enhancing flexibility‚ and improving strength. This method accelerates the return to sports activities by restoring proper movement and reducing the risk of re-injury‚ making it a preferred choice for athletes seeking effective rehabilitation.
5.3 Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) plays a crucial role in post-surgical rehabilitation by restoring mobility and function. It employs manual techniques to address joint and soft tissue restrictions‚ promoting healing and reducing scar tissue formation. FMT also incorporates neuromuscular re-education to enhance strength and motor control‚ tailored to individual recovery needs. This approach accelerates the return to daily activities and improves overall functional outcomes‚ making it an essential component of post-surgical care.

Comparison with Other Manual Therapies
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) stands out for its integrated approach‚ combining manual techniques with neuromuscular and motor control strategies. Unlike chiropractic care‚ which focuses on spinal alignment‚ or osteopathic manipulative therapy‚ which emphasizes whole-body wellness‚ FMT uniquely blends mechanical‚ neuromuscular‚ and motor control systems for comprehensive care. Its patient-centered‚ evidence-based methods distinguish it from traditional physical therapy‚ offering a holistic treatment approach.
6.1 FMT vs. Chiropractic Care
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) differs from chiropractic care in its holistic approach‚ focusing on manual techniques to address mechanical‚ neuromuscular‚ and motor control systems. While chiropractic care emphasizes spinal manipulation and joint alignment‚ FMT integrates soft tissue mobilization‚ visceral techniques‚ and neuromuscular re-education. FMT prioritizes patient-centered‚ evidence-based methods‚ offering a broader scope of treatment beyond spinal adjustments‚ making it a distinct approach in manual therapy.
6.2 FMT vs. Osteopathic Manipulative Therapy
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) and Osteopathic Manipulative Therapy (OMT) share manual techniques but differ in approach. FMT focuses on mechanical capacity‚ neuromuscular function‚ and motor control‚ offering a structured‚ evidence-based system. OMT‚ part of osteopathic medicine‚ emphasizes the musculoskeletal system and overall health. While FMT is typically provided by physical therapists‚ OMT is performed by osteopathic physicians‚ blending manual techniques with philosophical principles of body unity and self-healing potential.
6.3 FMT vs. Traditional Physical Therapy
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) differs from traditional physical therapy by its emphasis on manual techniques and a structured‚ holistic approach. While traditional PT often focuses on exercises and modalities‚ FMT prioritizes hands-on methods to address mechanical‚ neuromuscular‚ and motor control issues. FMT’s systematic evaluation and treatment framework‚ developed by the Institute of Physical Art‚ offers a specialized approach that complements traditional methods‚ providing a unique‚ integrated solution for movement dysfunctions and pain management.
Integration of Eastern and Western Medicine
Functional Manual Therapy integrates Eastern and Western medicine by combining manual techniques with holistic approaches‚ emphasizing balance‚ nutrition‚ and lifestyle education for comprehensive care.
7.1 Principles of Eastern Medicine in FMT
Functional Manual Therapy incorporates Eastern medicine principles‚ emphasizing harmony‚ energy flow‚ and holistic healing. It integrates manual techniques with concepts like balance‚ nutrition‚ and lifestyle‚ focusing on the interconnectedness of body systems. This approach aligns with Eastern practices by addressing the whole person‚ promoting natural healing‚ and enhancing overall well-being through a blend of hands-on therapy and mindful care.
7.2 Combining Manual Techniques with Holistic Approaches
Functional Manual Therapy seamlessly integrates manual techniques with holistic approaches‚ blending hands-on methods with lifestyle and nutritional guidance. This fusion addresses the body as a whole‚ promoting balance and optimal function. By combining physical interventions with mindfulness and wellness practices‚ FMT enhances mobility‚ reduces pain‚ and supports long-term health‚ offering a comprehensive path to recovery and well-being.

Case Studies and Success Stories
Functional Manual Therapy has transformed lives‚ alleviating chronic pain‚ enhancing athletic performance‚ and aiding post-surgical recovery. Real-life successes highlight its effectiveness in restoring function and mobility.
8.1 Patient Outcomes in Chronic Pain
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) has shown remarkable success in managing chronic pain‚ with patients experiencing significant reduction in discomfort and improved mobility. By addressing the root causes of pain through manual techniques and neuromuscular re-education‚ FMT helps restore function and enhance quality of life. Many patients report long-term relief and improved ability to perform daily activities‚ highlighting FMT’s effectiveness in chronic pain management.
8.2 Improvements in Athletic Performance
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) significantly enhances athletic performance by improving joint mobility‚ reducing muscle imbalances‚ and optimizing movement patterns. Athletes experience increased strength‚ flexibility‚ and endurance‚ leading to better overall performance. FMT also reduces injury risk and accelerates recovery‚ allowing athletes to maintain peak condition. By addressing mechanical and neuromuscular inefficiencies‚ FMT helps athletes achieve their full potential and perform at higher levels in their respective sports.
8.3 Recovery from Post-Surgical Conditions
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) plays a crucial role in post-surgical recovery by enhancing mobility‚ reducing pain‚ and restoring function. Patients benefit from personalized treatment plans that address mechanical and neuromuscular limitations. FMT techniques‚ such as soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization‚ promote healing and improve range of motion. This approach helps patients regain strength‚ flexibility‚ and motor control‚ enabling a faster and more effective return to normal activities and overall recovery.

Evidence-Based Research and Outcomes
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) is supported by clinical studies demonstrating its effectiveness in improving mobility‚ reducing pain‚ and enhancing neuromuscular function. Research highlights long-term benefits.
9.1 Clinical Studies on FMT Effectiveness
Clinical studies validate the effectiveness of Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) in improving mobility‚ reducing pain‚ and enhancing neuromuscular function. Research demonstrates significant improvements in patients with chronic pain and movement dysfunctions. FMT’s holistic approach‚ focusing on mechanical‚ neuromuscular‚ and motor control systems‚ is supported by evidence-based methods. Long-term benefits‚ including enhanced quality of life‚ highlight FMT’s role in addressing musculoskeletal and functional limitations effectively.
9.2 Research on Neuromuscular and Motor Control
Research highlights FMT’s role in enhancing neuromuscular function and motor control. Studies demonstrate improved muscle initiation‚ strength‚ and endurance‚ enabling better movement patterns. FMT’s focus on neuromuscular re-education and motor control helps restore efficient brain-body communication‚ addressing musculoskeletal issues and promoting functional recovery. Evidence-based methods and clinical reasoning optimize these outcomes‚ making FMT a valuable approach for improving mobility and reducing pain.
9.3 Long-Term Benefits of FMT
Functional Manual Therapy offers sustained improvements in mobility‚ strength‚ and overall function. Long-term benefits include reduced chronic pain‚ enhanced movement patterns‚ and improved quality of life. FMT’s focus on restoring mechanical capacity‚ neuromuscular function‚ and motor control promotes lasting recovery. Patients often experience prolonged relief from musculoskeletal issues‚ enabling better participation in daily activities and sports‚ with reduced risk of recurrence.

The Future of Functional Manual Therapy
Functional Manual Therapy is evolving with advancements in manual techniques‚ integration of emerging technologies‚ and expanded applications in healthcare‚ enhancing its role in patient care and recovery.
10.1 Advancements in Manual Therapy Techniques
Advancements in Functional Manual Therapy techniques focus on integrating Eastern and Western medical principles‚ emphasizing holistic approaches. Innovations include refined soft tissue mobilization methods and precise joint mechanics assessments. The Institute of Physical Art (IPA) continues to pioneer these developments‚ ensuring therapists are equipped with cutting-edge‚ evidence-based skills to address complex musculoskeletal and neuromuscular conditions‚ enhancing patient outcomes and promoting long-term functional recovery.
10.2 Integration with Emerging Technologies
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) is evolving through integration with emerging technologies‚ such as AI-driven assessment tools and wearable devices. These innovations enhance precision in identifying movement dysfunctions and monitoring progress. Virtual reality and real-time biofeedback systems are also being explored to optimize manual techniques and patient engagement. This fusion of technology and hands-on therapy promises to revolutionize treatment outcomes‚ making FMT more accessible and effective for diverse patient populations.
10.3 Expanding Applications in Healthcare
Functional Manual Therapy (FMT) is increasingly being integrated into diverse healthcare settings‚ addressing chronic pain‚ sports injuries‚ and post-surgical recovery. Its versatility extends to pediatrics‚ geriatrics‚ and neurological rehabilitation‚ offering tailored solutions for complex conditions. By combining manual techniques with holistic approaches‚ FMT enhances traditional therapies‚ making it a valuable tool for multidisciplinary teams aiming to improve patient outcomes and overall well-being across various demographics and medical specialties.