A swimming training program offers a structured approach to improving technique, endurance, and overall performance in the water, benefiting both recreational and competitive swimmers alike effectively.
1.1 What is a Swimming Training Program?
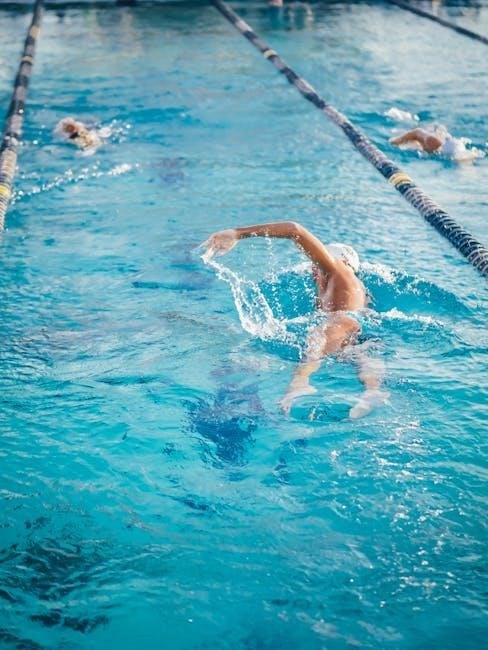
A swimming training program is a structured plan designed to enhance swimming performance, endurance, and technique. It typically includes goal setting, warm-ups, drills, and strength exercises tailored to individual needs. Whether for competitive athletes or recreational swimmers, these programs aim to improve overall fitness and aquatic skills. They often incorporate stroke refinement, speed drills, and conditioning to ensure balanced development. A well-designed program helps swimmers progress systematically, achieving their objectives effectively while minimizing the risk of injury or burnout.
1.2 Importance of Structured Training
Structured training is essential for swimmers to avoid plateaus and prevent overtraining. It ensures consistent progress, helping swimmers stay motivated and focused on their goals. A well-organized plan also reduces the risk of injuries by balancing intensity and recovery. Additionally, structured programs often incorporate cross-training, such as running, to enhance overall fitness. This approach supports long-term development, making it easier for swimmers to adapt to new challenges and achieve their objectives effectively over time.

Benefits of a Swimming Training Program
A swimming training program enhances cardiovascular fitness, builds muscle, and improves mental well-being, offering a comprehensive workout that supports overall health and longevity effectively.
2.1 Improved Cardiovascular Health
Swimming is an excellent way to improve cardiovascular health by strengthening the heart and lungs. Regular sessions lower resting heart rate and increase stroke volume, enhancing overall circulation. The low-impact nature makes it ideal for all fitness levels, reducing joint strain. Consistent training boosts endurance, allowing for longer and more intense workouts. Over time, swimmers experience improved blood flow and reduced risk of heart disease, contributing to a healthier lifestyle.
2.2 Increased Muscle Strength and Endurance
Swimming effectively builds muscle strength and endurance by engaging multiple muscle groups simultaneously. The water’s resistance provides a natural workout, toning muscles without excessive strain. Regular swimming enhances endurance as muscles adapt to sustained activity, improving overall physical resilience. Different strokes target specific areas, ensuring a balanced workout. Over time, swimmers develop stronger, leaner muscles and increased stamina, making it an ideal activity for full-body conditioning and long-term physical fitness.
2.3 Enhanced Flexibility and Mobility
Swimming is a low-impact exercise that enhances flexibility and mobility by allowing a wide range of motion in the water. The buoyancy of water reduces joint stress, making it ideal for improving flexibility without strain. Different strokes target various muscle groups, promoting a full-body stretch and increasing mobility. Regular swimming helps maintain joint health, making it easier to perform daily activities and other sports. This makes it a great option for people seeking to improve their overall flexibility and movement efficiency naturally.
2.4 Weight Management and Toning
Swimming is an effective way to manage weight and tone muscles due to its calorie-burning and resistance-building properties. The water provides natural resistance, helping to strengthen and define muscles without bulk. Regular swimming sessions can boost metabolism, aiding in weight loss and maintenance. It also improves body composition by reducing fat and increasing lean muscle mass, leading to a more toned and streamlined physique. This makes swimming a versatile and efficient option for those looking to achieve their weight and fitness goals.
Components of a Swimming Training Program
A well-rounded swimming program includes goal setting, warm-ups, technique drills, endurance exercises, and strength training, ensuring a balanced approach to skill development and physical fitness.
3.1 Goal Setting and Objectives
Setting clear, achievable goals is crucial for swimmers to stay motivated and track progress. Whether aiming to improve lap times or master specific strokes, defining objectives helps create a focused training plan. SMART goals—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound—ensure swimmers have a roadmap to success. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these goals keeps the training program dynamic and aligned with evolving aspirations, fostering continuous improvement and a sense of accomplishment.
3.2 Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines
A proper warm-up prepares the body for swimming by increasing heart rate and flexibility, reducing injury risk. It typically includes light cardio and dynamic stretches. Conversely, a cool-down helps gradually lower heart rate and relax muscles, preventing stiffness. Both routines are essential for optimizing performance and ensuring long-term physical health. Incorporating these practices into a swimming training program enhances overall efficiency and supports recovery, making them integral components of any effective regimen for swimmers at all levels.
3.3 Stroke Technique and Efficiency
Mastering stroke technique is crucial for swimmers, as it enhances speed, reduces energy expenditure, and minimizes injury risk. Proper body positioning, arm and leg movements, and breathing synchronization are key. Drills like catch-up and fingertip drag help refine strokes, while feedback from coaches or video analysis provides personalized improvement opportunities. Efficient technique allows swimmers to swim longer distances with less fatigue, making it a cornerstone of any effective swimming training program aimed at achieving peak performance and longevity in the sport.
3.4 Speed and Endurance Drills
Speed and endurance drills are essential for swimmers aiming to enhance performance. Sprint intervals and timed laps improve speed, while longer distances at a steady pace build endurance. Incorporating drills like 50-meter sprints or 400-meter repeats helps swimmers adapt to race-like conditions. These exercises not only boost cardiovascular fitness but also mental resilience, enabling swimmers to maintain consistency during competitions. Balancing speed and endurance training ensures a well-rounded approach to swimming, making it a vital component of any structured program.
3.5 Strength and Conditioning Exercises
Strength and conditioning exercises are crucial for swimmers to build power and durability. Dryland training, including resistance bands and weightlifting, targets key muscle groups like shoulders and legs. These exercises enhance swimming performance by improving stroke efficiency and overall power. Incorporating core workouts and plyometrics also boosts stability and explosiveness in the water. Regular strength training not only enhances speed and endurance but also reduces the risk of injuries, making it a cornerstone of a comprehensive swimming program.

Designing a Personalized Swimming Training Program
Designing a personalized swimming training program involves assessing fitness levels, setting specific goals, and creating a tailored plan that incorporates cross-training and progressive overload for optimal results.
4.1 Assessing Current Fitness Levels
Assessing current fitness levels is crucial for designing an effective swimming program. This involves evaluating endurance, strength, and technique through timed swims and strength tests. Understanding a swimmer’s abilities helps tailor workouts to their needs, ensuring progress and reducing injury risks. Incorporating cross-training, like running, can enhance overall fitness. Regular reassessments track improvements and adjust the program accordingly, keeping goals achievable and motivation high throughout the training journey.
4.2 Creating a Customized Workout Plan
A customized workout plan aligns with the swimmer’s goals and fitness level, ensuring targeted improvement. It involves setting specific objectives, breaking them into manageable parts, and focusing on technique, endurance, and strength. Incorporating cross-training activities, like running, can enhance overall fitness. The plan should include varied drills, intervals, and rest periods. Regular progress evaluations allow adjustments to maintain challenge and engagement. A well-tailored plan ensures steady improvement and keeps swimmers motivated to achieve their swimming aspirations effectively;
4.3 Incorporating Cross-Training Activities
Incorporating cross-training activities, such as running or strength exercises, enhances swimming performance by improving overall fitness and reducing injury risk. These activities complement water-based workouts by building endurance, strength, and flexibility. For example, running boosts cardiovascular health, while weight training strengthens muscles used in swimming. Cross-training also prevents overuse injuries by diversifying physical demands. By integrating these activities into a swimming training program, athletes achieve a balanced and well-rounded approach to their sport, leading to better overall results and longevity in their swimming careers effectively.
Progress Tracking and Evaluation
Regularly assessing performance and progress ensures swimmers stay on track, allowing for timely adjustments and celebrating milestones to maintain motivation and achieve long-term goals effectively.
5.1 Monitoring Workout Progress
Monitoring workout progress is essential for swimmers to track improvements and stay motivated. Regularly recording lap times, stroke counts, and heart rates provides measurable data to assess performance. Using tools like swim logs or mobile apps helps maintain consistency and accountability. Coaches and swimmers can identify strengths and areas for improvement, ensuring workouts remain challenging yet achievable. Progress tracking also helps adjust training plans dynamically, keeping swimmers engaged and focused on their goals. Celebrating small milestones boosts morale and encourages continued effort in the program.
5.2 Adjusting the Training Plan

Adjusting the training plan ensures swimmers stay on track and continue making progress. Periodically reassessing goals and performance allows for modifications to intensity, volume, or focus areas. Incorporating cross-training, like running, can enhance endurance and reduce injury risk. Coaches may introduce new drills or techniques to keep workouts engaging. Regular adjustments prevent plateaus and maintain motivation, ensuring the program remains challenging and aligned with the swimmer’s evolving needs and aspirations throughout the season.
5.3 Setting Milestones and Celebrating Achievements
Setting milestones helps swimmers track progress and stay motivated. Celebrating achievements, no matter how small, boosts confidence and reinforces commitment to the training program. Recognizing improvements in technique, speed, or endurance creates a sense of accomplishment. This positive reinforcement encourages swimmers to push harder and maintain consistency. Milestones also provide a clear roadmap, making the journey feel purposeful and rewarding, which is essential for long-term success in swimming training programs.

Nutrition and Recovery in Swimming Training
Proper nutrition and recovery are vital for swimmers, ensuring energy replenishment and muscle repair. A balanced diet, hydration, and adequate rest support optimal performance and injury prevention effectively.
6.1 Proper Diet for Swimmers
A proper diet for swimmers should include a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to fuel workouts and aid recovery. Carbohydrates provide energy, while proteins repair muscles. Incorporating lean meats, fish, eggs, and plant-based options ensures adequate protein intake. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables supply essential vitamins and minerals. Hydration is also crucial, with swimmers needing to drink plenty of water before, during, and after training sessions to maintain performance and overall health effectively.
6.2 Hydration Strategies
Proper hydration is essential for swimmers to maintain performance and health. Aim to drink 17-20 ounces of water 2-3 hours before training and 8-10 ounces every 10-15 minutes during workouts. Monitor urine color; pale yellow indicates adequate hydration. Avoid overhydration, which can lead to hyponatremia. Carry a water bottle to track intake and refill regularly. Coaches often emphasize hydration as a key component of overall training success, ensuring swimmers stay energized and focused throughout their sessions.
6.3 Recovery Techniques and Rest
Recovery is crucial for swimmers to repair muscles and enhance performance. Incorporate stretching, yoga, or foam rolling to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension. Ensure 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly to aid muscle repair and mental rejuvenation. Active recovery, such as light jogging or cycling, can also promote blood flow without overexertion. Nutrition plays a key role; consume a balanced diet rich in protein to support muscle repair. Neglecting recovery can lead to injuries and decreased performance, making rest a vital component of any training program.

Avoiding Injuries in Swimming Training
Injury prevention is essential for swimmers to maintain consistency and performance. Proper warm-ups, technique adjustments, and strength training can significantly reduce the risk of common swimming-related injuries effectively.
7.1 Common Injuries in Swimmers
Swimmers often face injuries like shoulder tendinitis, rotator cuff strains, and lower back pain due to repetitive strokes and overuse. Proper technique, strength training, and adequate rest can help prevent these issues, ensuring long-term swimming health and performance.
7.2 Preventative Measures and Exercises
Preventative measures include strengthening shoulder stability with exercises like scapular push-ups and rotational exercises. Incorporating core workouts and flexibility routines can reduce injury risk. Swimmers should also focus on proper stroke technique and avoid overtraining. Cross-training activities, such as running or cycling, can enhance overall fitness without overloading swimming muscles. Regular stretching and warm-up routines are essential to maintain muscle health and prevent strains, ensuring a safer and more effective swimming experience.
7.3 Rehabilitation Techniques
Rehabilitation techniques for swimmers focus on restoring strength and mobility after injuries. Low-impact exercises, such as light freestyle laps or water aerobics, can aid recovery without strain. Stretching routines, including shoulder and hip flexor stretches, improve flexibility. Strengthening exercises like pull-ups and core workouts help rebuild muscle stability. Physical therapy sessions can address specific injuries, while taping or bracing may provide additional support. Incorporating cross-training, such as cycling or yoga, enhances recovery and prevents future injuries, ensuring a safe return to competitive swimming.
Mental Preparation and Focus
Mental preparation is crucial for swimmers, enhancing resilience and concentration. Techniques like visualization and positive affirmations help build confidence, while setting achievable goals maintains motivation and focus.

8.1 Building Mental Toughness
Mental toughness is essential for swimmers to overcome challenges and perform under pressure. Techniques like visualization, positive self-talk, and goal-setting help build resilience. Embracing a growth mindset allows swimmers to view setbacks as opportunities for improvement. Regular mindfulness practices can enhance focus and reduce anxiety, ensuring a strong mental foundation for peak performance in training and competitions. Consistent mental training fosters confidence and determination, key attributes for success in swimming.
8.2 Visualization Techniques
Visualization is a powerful tool for swimmers to mentally rehearse races and techniques, enhancing performance. By vividly imagining successful strokes and race scenarios, swimmers build confidence and muscle memory. This practice reduces race-day anxiety and improves focus. Regular visualization sessions, even a few minutes daily, can significantly impact mental preparedness and physical execution in the water, making it a valuable addition to any training program.
8.3 Staying Motivated and Focused
Staying motivated and focused in a swimming training program requires setting realistic goals and celebrating small achievements. Surround yourself with a supportive team or coach to maintain morale. Track progress through logs or apps to see improvements, which can be a powerful motivator. Incorporate variety in workouts to avoid monotony and prevent burnout. Remember, consistency and mental strategies like positive self-talk are key to staying driven and focused on your swimming objectives over time.
A well-structured swimming training program enhances physical fitness, mental discipline, and overall well-being, making it a transformative journey for swimmers of all levels and goals consistently.
9.1 Summary of Key Points
A swimming training program is a structured plan that enhances cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and flexibility while promoting weight management. It includes goal setting, proper techniques, and cross-training like running to boost performance. Nutrition, hydration, and recovery are crucial for optimal results. Consistency and mental focus are key to achieving milestones and avoiding injuries. Whether for recreation or competition, a well-designed program fosters overall well-being and transforms swimming into a rewarding lifelong activity with measurable progress and lasting benefits.
9.2 Final Tips for Success
Stay committed to your swimming training program and track progress consistently. Incorporate cross-training, like running, to enhance endurance and strength. Listen to your body, ensuring proper rest and recovery to avoid injuries. Maintain a balanced diet and stay hydrated for optimal performance. Set realistic goals and celebrate small victories to stay motivated. Mental preparation and focus are key—visualize success and embrace challenges with confidence. With dedication and persistence, you’ll achieve your swimming goals and enjoy a lifelong journey of health and achievement.